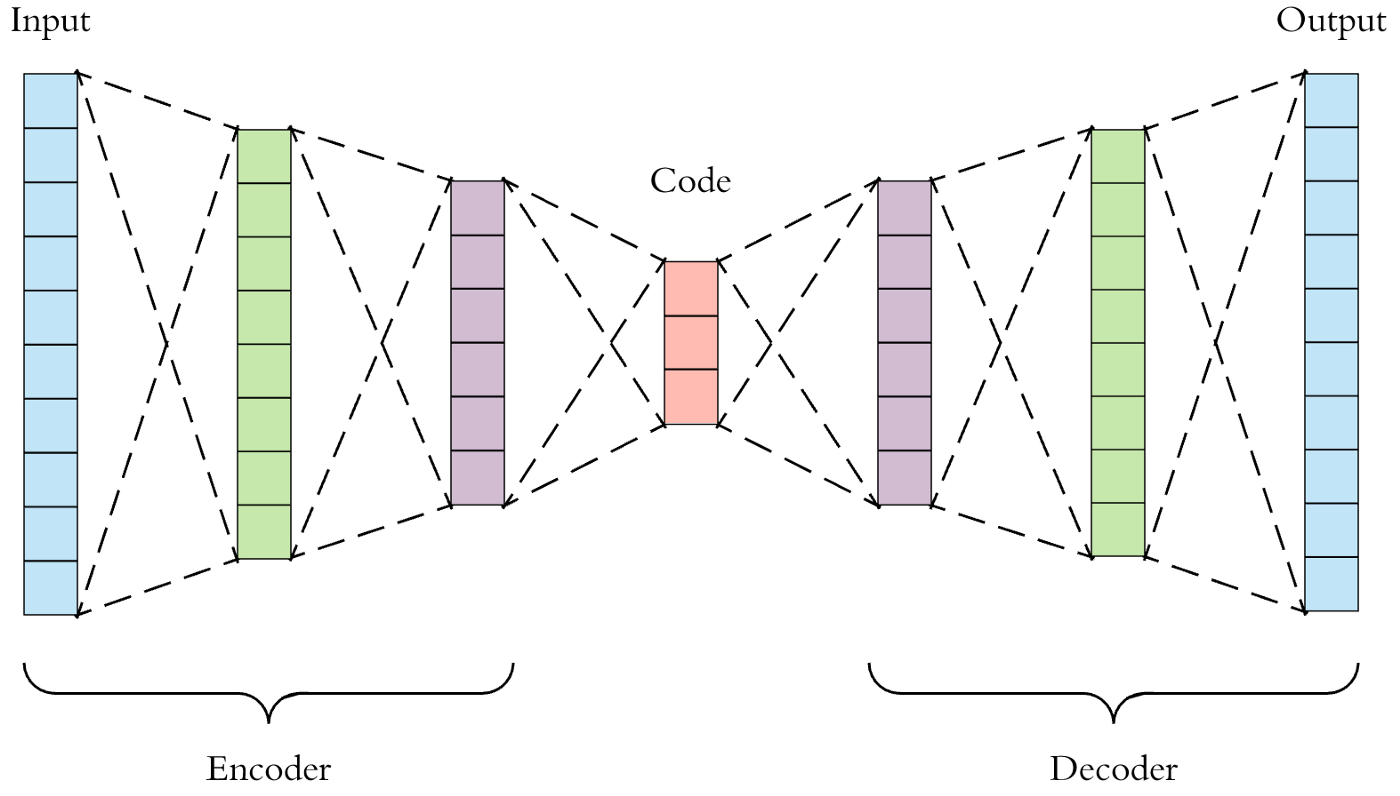
An autoencoder is a type of feedforward neural network that attempts to copy its input to its output. Internally, it has a hidden layer, h, that describes a code, used to represent the input. The network consists of two parts:
- An encoder function: h=f(x).
- A decoder function, that produces a reconstruction: r=g(h).
The figure below shows the autoencoder architecture. First, the input passes through the encoder, which is a fully-connected neural network, in order to produce the code. The decoder, which has the similar neural network structure, then produces the output by using the code only. The aim is to get an output identical to the input.
In order to build an autoencoder, three things are needed: an encoding method, a decoding method, and a loss function to compare the output with the target.