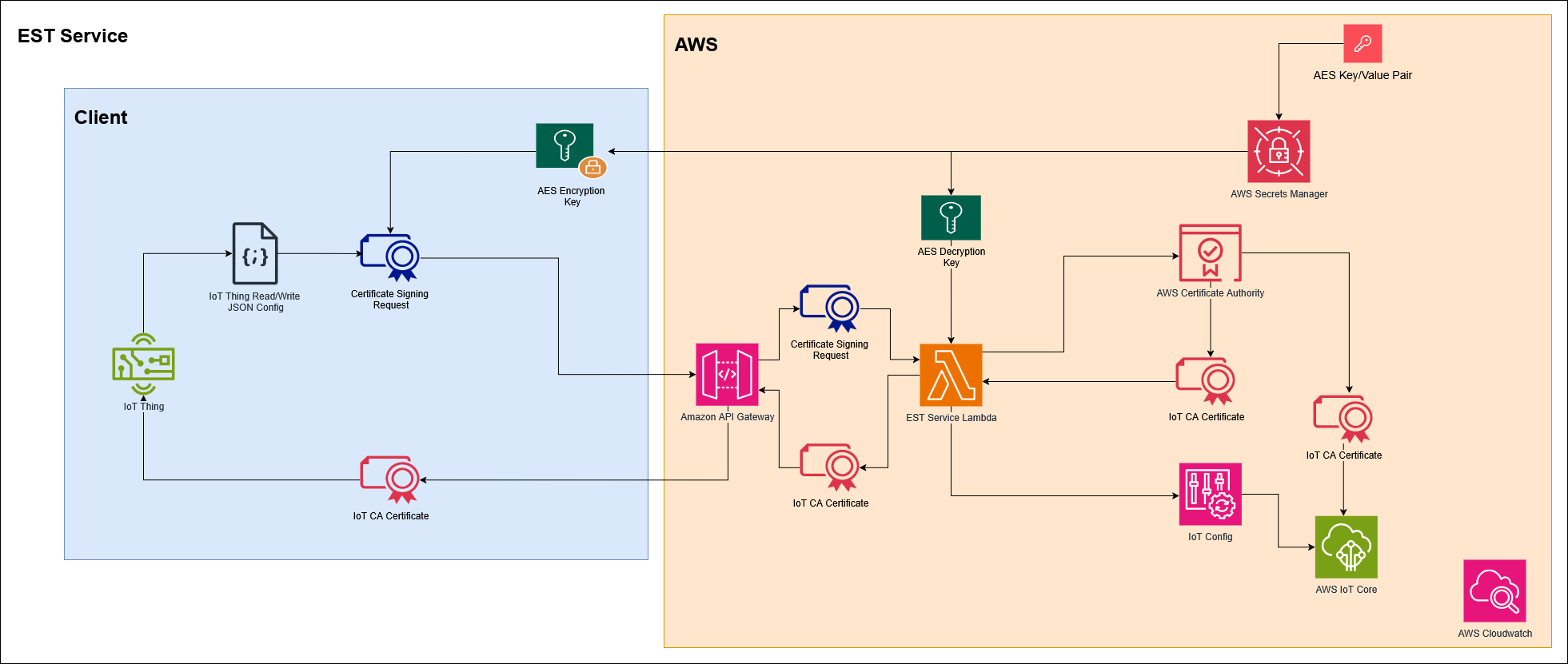
EST (Enrolment over Secure Transport) provides a standards-based way to issue X.509 certificates to IoT devices. In this architecture, EST removes the need for pre-shared keys or manual certificate distribution by letting each device generate its own keys, submit a certificate signing request (CSR), and receive a signed certificate over TLS. This gives every device a unique, provable identity and enables secure enrollment at scale. It also supports fine-grained Identity and Access Management (IAM) at the device level, and full auditability through logging - all of which are essential in regulated environments.
In this implementation, AWS services were used to provide secure, automated certificate enrollment for IoT devices.
- Each device generates its own key pair locally and prepares a configuration file that defines the device name and IAM permissions.
- This configuration is wrapped in an Object Identifier (OID) and used to create a CSR, encrypted with AES.
- The encrypted CSR is sent to AWS through an API Gateway, which invokes a Lambda function.
- Lambda retrieves the AES key from the Secrets Manager, decodes the CSR, signs it and registers the device in AWS IoT Core with the appropriate certificate and permissions.
- All activity is recorded in CloudWatch, ensuring that certificate requests, approvals, and device registrations are fully auditable.
The enrolment process can be broken into six steps:
- The IoT Thing generates its own key pair and a configuration file with its identity and permissions.
- The Thing creates a CSR, encrypts it with AES, and sends it to the enrolment service via an API Gateway.
- The enrolment service retrieves the AES Key, decrypts the CS, and validates the request.
- The CSR is signed by the Certificate Authority, producing an IoT Certificate.
- The IoT Config file, along with the signed certificate, is used for the creation of the IoT Thing.
- The signed certificate, along with the IoT CA certificate, is returned to the Thing.
- All activity is logged for auditing.