Team Leaders: Anujit Sarkar, Agaz Wani
Team Members: Ashley Lui, Zoe Taylor, Jiyoun Yoo, Krishna Sharma, Nicole Avalon, Peter Radulovic, Ashley Denslow, Yibo Dong
GVN/USF mentors:
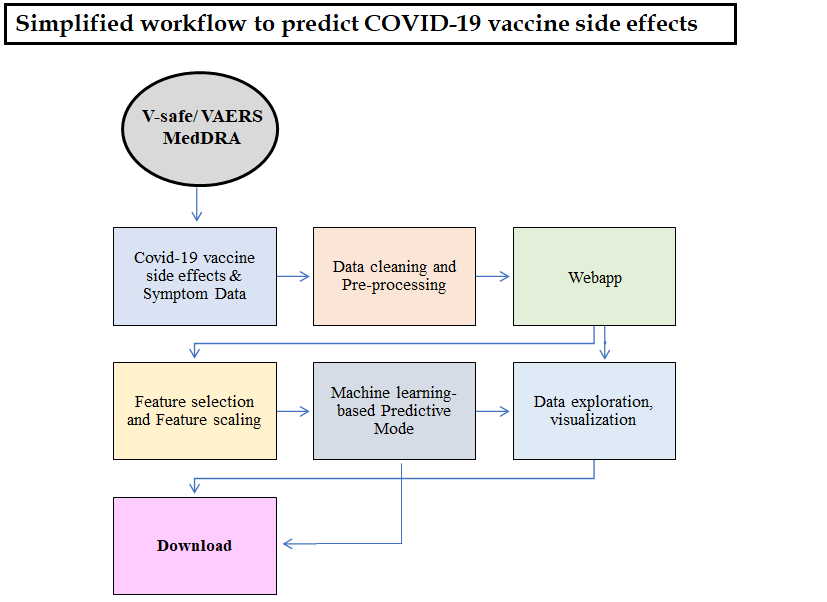
Our objective in this project is to design a predictive model based on machine learning for the adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccination in US. We will usee the relevant data (primarily metadata and disease history) stored in Vaccine adverse events reporting system (VAERS) managed by CDC. Finally, we would like to create an web app for the users to predict the possible adverse effect which they might experience post vaccination.
Data Pre-Processing:
To develop our predictive model, we obtained data on patient demographics, vaccinations, and reported symptoms from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) 2021 data sets, processed up to February 12th 2021. The three sets from VAERS were cross-referenced and merged into a single spreadsheet consisting of 8,582 patient entries covering 12,617 features. Reported symptoms were codified using hierarchical categorization based on the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities Terminology (MedDRA®) standard system, which is the international medical terminology developed under the auspices of the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). MedDRA® trademark is registered by ICH.
Feature Selection & Data Normalization:
Patient demographic metadata underwent a Chi-Squared significance test to pre-select features that correlated with adverse events. The selected features then underwent MinMax scaling to normalize the data for use in training a machine learning model.
Machine Learning Model:
For our machine learning model we utilized a support vector machine algorithm.
- Memory: > 4GB
- Python 3
- Sklearn
- Django 3.1.7
- boostrap 3.4.1
- Javascript
We found some critical features that predict vaccine adverse events such as life-threatening illness, hospitalization, deaths, etc. Medication intake and allergies to different medications play a significant role in the prediction. Also, alcohol usage is a strong predictor for outcome variables.
Machine Learning models worked very well in predicting the adverse events due to the Covid-19 vaccine. We found essential features that derive the prediction. More work is needed to relate the features to the clinical outcome to help the clinicians in decision-making.